The National Medical Commission (NMC) has released the Guidelines For Competency Based Postgraduate Training Programme For DM In Pediatric Nephrology.
1. While there has been improvement in nutritional status and immunization coverage over the last three decades, chronic non-communicable diseases involving various systems are now becoming an important cause of mortality and morbidity in childhood. There is an increasing demand for specialized care of children with chronic diseases. Children with kidney diseases are often diagnosed and referred in late stages of the disease. Most of them are not treated appropriately due to lack of expertise and want of diagnostic and therapeutic infrastructure. A phenomenal progress has taken place that has revolutionized management of children with renal diseases.
The country have been largely denied the benefits of advanced medical management. For pediatricians to provide optimal treatment for these children, special training and in-depth knowledge are necessary. It is imperative to provide suitable facilities for appropriate and relevant training in pediatric nephrology to promote growth of the specialty in the country. The training should emphasise on preventive aspects, early diagnosis of common diseases and their optimum management with available resources including dialysis and transplantation. The primary goal of the training programme for DM in Pediatric Nephrology is to develop clinicians who have acquired the operational skills, professionalism and knowledge necessary to direct a pediatric nephrology service, including dialysis and kidney transplantation.
The program includes 36 months of training and is designed to provide the experiences necessary for the DM students to develop the knowledge and skills to function as an independent pediatric nephrologist and fulfill the requirements as mandated by the Medical Council of India.
Eligibility for admission: M.D in Pediatrics
Goals:
The goal of the course shall be to produce a competent specialist in the area of Pediatric Nephrology:
1. who shall be competent to handle the health needs of patients in the speciality and provide secondary and tertiary level of care,
2. who shall be able to practice the speciality ethically,
3. who shall be aware of the contemporary advances and developments in the subject,
4. who shall acquire a spirit of scientific inquiry and is oriented to the principles of research methodology and epidemiology, and
5. who shall have acquired the skills for teaching medical and paramedical professionals.
A. Objectives:
The objectives of the training programme will be to enable the student:
1. To develop a scientific approach, based on the understanding of the pathophysiology and epidemiology of pediatric renal disease,
2. To provide primary, secondary and tertiary care to children with renal disease,
3. To provide the skills for management of emergencies in unstable children with renal problems and provide renal care to critically ill children in the intensive care unit,
4. To implement a follow up plan in children with chronic disease,
5. To be able to work in a team along with intensivists, pediatricians, pediatric surgeons and others to provide comprehensive care to children with renal disease,
6. To be able to set up and manage an independent Pediatric Nephrology unit including dialysis,
7. To develop adequate communication and counselling skills,
8. To recognize the importance of family, society and socio-cultural environment in the treatment of the sick child with renal disease,
9. To review and analyse literature, seek evidence and apply to clinical practice,
10. To develop basic research skills and carry out research projects in the field of Pediatric Nephrology, and
11. To develop basic teaching skills and be able to train undergraduates, postgraduates, nursing and paramedical staff regarding care of children with renal disease.
2. SUBJECT SPECIFIC LEARNING OBJECTIVES
• Cognitive Domain: Theoretical Knowledge
1) Understand the normal renal anatomy and physiology from fetal life to adolescence.
2) Understand the normal physiology and pathophysiology of body fluids, acid- base and electrolytes including neonates and infants.
3) Understand the basic principles involved in pathology of renal diseases in children and their assessment as applicable to pediatric nephrology practice.
4) Understand the basics of pathologic interpretation of the biopsy, including all the components: light, immunofluorescence, electron microscopy and immuno-histochemical staining.
5) Be conversant with the etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of common neonatal and pediatric renal diseases in an out -patient, inpatient and emergency settings.
6) Demonstrate knowledge about biomedical, clinical and cognate sciences and how to apply them in the management of children with kidney diseases.
7) Know and apply the basic and clinically supportive sciences and present evidence-based recommendations for diagnostic and therapeutic decision making in children with renal diseases.
8) Recognize the importance of inter-disciplinary approach in the management of various pediatric renal diseases and obtain relevant specialist / ancillary services’ consultation where appropriate.
9) Acquire knowledge for the prevention of renal diseases in children.
• Practical and Clinical skills
1) Understand the presentation (history and clinical examination), evaluation and management of congenital and acquired renal disorders in neonates, infants and children.
2) Order relevant investigations and competently interpret the results of laboratory studies including urinalysis and the results of general and renal imaging procedures performed in children with kidney and urinary tract disorders.
3) Formulate and implement treatment plans, and monitor the effectiveness of their interventions for various renal diseases including management of acute
kidney injury, chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in a holistic manner.
4) Perform competently all medical and invasive procedures, i.e., (a) percutaneous renal biopsy of native and transplanted kidneys, (b) placement of temporary vascular access or peritoneal catheter for renal replacement therapy (RRT), (c) Perform hemodialysis, acute and chronic peritoneal dialysis and continuous renal replacement therapy, and (d) Urine analysis.
5) Develop desired skills to independently manage emergency situations related to renal disease.
6) Communicate effectively and demonstrate caring and respectful behavior when interacting with children with renal and urinary tract problems and their families.
7) Be conversant with counseling techniques for the family / primary care takers.
8) Work with faculty and colleagues to provide patient-focused care.
9) Perform necessary patient care documentation in an accurate and timely manner.
10) Develop skills as a self‐directed learner, recognize continuing educational needs and use appropriate learning resources to critically analyze relevant published literature in order to practice evidence‐based medicine.
• Writing Research articles
1) Demonstrate competence in basic concepts of research methodology and epidemiology and be able to critically analyse relevant published research literature,
2) Locate, appraise and assimilate evidence from scientific studies,
3) Develop the expertise to perform a scientific study including formulating hypothesis, research questions, designing appropriate study, analyze and interpret the results,
4) Ability to write an in-depth manuscript describing a completed project,
5) Publication or presentation of case reports or clinical series at local, regional, or national professional and scientific society meetings.
• Attitudes including communication skills
1) Demonstrate respect, compassion, and integrity; a responsiveness to the needs of patients and society; and a commitment to excellence.
2) Demonstration of skill in listening to patients and families and the ability to effectively educate and counsel patients and their families on diagnostic and treatment decisions including initiation of dialysis therapies and prognosis.
3) Develop the skills to interact with professional colleagues for the care of the renal patient.
4) Demonstrate the ability to lead the consult service through interactions with referring and primary doctor.
5) Effectively work with other members of the health care team, including referring physicians from other specialties, nurses, social workers and technicians, to implement a treatment plan.
6) Effectively teach pediatric nephrology care to medical students, junior post graduate students and nurses.
7) Adopt ethical principles in all aspects of pediatric nephrology practice/ research. (Professional honesty and integrity, humility, informed consent, counseling and recognize patients’ rights and privileges).
• Training in Research Methodology
1) Attend research methodology course to learn framing of research question, designing and conducting study, analysing and interpreting data and writing a paper.
2) Participate in on-going research activities of the department to obtain experience in various aspects of research.
3) Apply knowledge of study designs and statistical methods to the appraisal of clinical studies and other information on diagnostic and therapeutic effectiveness.
4) Familiarize with ethics in research.
3. SYLLABUS
3.1 SUBJECT SPECIFIC THEORETICAL COMPETENCIES
3.1.1 Cognitive domain (Knowledge domain)
3.1.2 Affective domain (Attitudes including Communication and Professionalism)
3.2 SUBJECT SPECIFIC PRACTICE BASED OR PRACTICAL COMPETENCIES
The curriculum outlines competences that trainees must reach by the end of the programme (combining 3.1 and 3.2)
A. Investigation of the kidney
1. Renal Anatomy and Physiology
|
Knowledge |
a. GFR from
c. Urinary d. Tubular handling of fluid and e. Acid-base balance
a. Creatinine clearance b. Protein and calcium excretion c. Tubular handling d. Tests for urinary acidification |
|
Skills |
To appropriately |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
Laboratory Medicine Department |
|
Resources |
Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders – Burton Principles of Renal Pediatric Renal Investigations – Chapman & |
1. Imaging
|
Knowledge |
· To understand the role of arteriography and percutaneous |
|
nephrostomy tube placement |
|
|
Skills |
· To appropriately request the different radiological investigations · To be able to interpret scan images |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
|
|
Resources |
· Bank of typical |
2. Renal Biopsy
and nephropathology
|
Knowledge |
· To describe the anatomy of both · To know · To describe the procedure of renal
red /immuno-fluroscence used in the diagnosis of renal disease. |
|
Skills |
· To perform a native (and transplant) biopsy safely
· Obtain adequate clinical background and |
|
appropriate nephrologist submitting the specimen to allow optimal interpretation of the |
|
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
Radiologist and pathologist |
|
Resources |
Nephropathology meetings Bank of typical case histology Training day samples |
(B)
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) and
Vesicoureteric Reflux
|
Knowledge |
· To know · To understand current theories about · To be aware of issues in diagnosis of UTI
· To understand the secondary progression of renal damage and prevention |
|
Skills |
· To show UTI, and possible management of siblings of children with |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
· To know · To recognize the role of microbiologists, urologists and radiologists
|
|
Resources |
· Microbiology department · Nephro-pediatric surgery-radiology meeting |
- Structural Malformations
|
Knowledge |
· To understand renal embryology and
· To know renal disease: structural as well |
|
Skills |
· To be able especially following relief of obstruction |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
· To show professionals |
|
Resources |
· Department of Pediatric Surgery · Radiology meeting · Department/Division of Neonatology |
(D)
Disorders of Micturition
|
Knowledge |
· To know
|
|
Skills |
· To know |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
· Liaison with · Role of the psychologist |
|
Resources |
Pediatric urologists/surgeons Bank of images |
(E) Neurogenic bladder
|
Knowledge |
· To know · To know
· To understand the treatments available to regularize bowel bladder habit |
|
Skills |
· To show urinary tract |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
· To know |
|
Resources |
· Pediatric urology |
(F)
Hematuria
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
|
|
urological assessment, and genetic and |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
|
(G) Proteinuria
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
|
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
|
(H)
Glomerular disease
|
Knowledge |
cytotoxic drugs, |
|
Skills |
nephritic syndrome, and new presentation of chronic |
|
glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
Resources |
|
(I) Nephrotic syndrome
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
measures to treat |
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
Liaison with |
|
Resources |
Pediatrics, Pathology |
(J)
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
patient with |
|
Multidisciplinary |
impact on reproductive potential |
|
Resources |
Adult nephrology, rheumatology services |
(K) Other Vasculitis
|
Knowledge |
adverse effects |
|
Skills |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
To work with |
|
Resources |
Pediatric and adult |
(L)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
|
|
Knowledge |
To list interstitial disease, and the relationship to systemic conditions |
|
Skills |
To appropriately investigate and manage interstitial nephritis, including use of corticosteroids |
(N)
Hypertension
|
Knowledge |
|
|
anti-hypertensive agents
|
|
|
Skills |
modify prescription |
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
|
(O) Nephrolithiasis
|
Knowledge |
management of renal stones (including lithotripsy) |
|
Skills |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
Departments of Laboratory Medicine, Pediatric Surgery, Urology and |
(P)
Tubular disorders
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
tubular disorders |
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
Metabolic clinics, Endocrine clinic Biochemistry department |
- Cystic disease
|
Knowledge |
kidney disease |
|
Skills |
disease |
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
|
(R)
Genetic disorders (Inherited diseases of the
kidneys)
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
diseases |
|
Multidisciplinary |
To understand the and counseling, including antenatal diagnosis |
|
Resources |
Geneticist |
(S) Fluid and electrolyte disturbances
|
Knowledge |
imbalance and their management |
|
Skills |
To be able to manage fluid and non-renal disease including overdose |
|
Resources |
|
(T)
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
|
|
the patient’s fluid status
disease requiring acute renal replacement therapy |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
Intensive care and neonatal |
(U) Chronic Kidney Disease
(CKD)
|
Knowledge |
erythropoietin and |
|
Skills |
|
|
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
in adult life |
|
Resources |
|
(V)
Transplantation
|
Knowledge |
Pre-Transplantation
blood grouping, HLA matching and donor-recipient cross |
|
matching
Transplantation
Post-Transplantation
|
|
|
Skills |
Pre-transplantation
Transplantation
Post-transplantation |
management on renal replacement therapy |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
To understand the role of the To appreciate the role |
|
Resources |
|
(W) DIALYSIS
1. Hemodialysis
|
Knowledge |
blood-borne viral |
|
Skills |
|
|
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
Resources |
Hemodialysis technician and nurses Departments of Nephrology, Microbiology and Surgery |
2. Peritoneal Dialysis
|
Knowledge |
infective and |
|
Skills |
|
|
|
|
Multidisciplinary aspects |
Pediatric surgeon |
(X)
Pharmacology
|
Knowledge |
immunosuppressive agents |
|
Skills |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
and reporting of problems with medication |
|
Resources |
Pharmacologists |
- Psychosocial and Ethical
issues
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
|
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
|
social worker,
|
|
|
Resources |
Multidisciplinary |
(Z)
Teaching skills
|
Knowledge |
|
|
Skills |
manuscript preparation |
(A1) Nutrition
|
Knowledge |
disease including those on dialysis and |
|
Skills |
children with |
|
Multidisciplinary |
|
Competency in Procedural /Practical Skills:
The post graduate student should be able to perform independently the following procedures
• Renal biopsy
Satisfactory performance of percutaneous biopsy of native and transplant kidneys entail:
- knowledge of indications for the procedure,
- obtaining informed consent,
- performance of the procedure itself including minimizing patient discomfort, and
- interpretation of results of the biopsy.
• Central venous access insertion for hemodialysis
Satisfactory placement of vascular access entails:
- knowledge of informed consent,
- proper Seldinger technique,
- knowledge of vascular anatomy,
- minimizing patient discomfort, as well as
- functional catheter placement and recognize/manage complications
• Acute peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion
Satisfactory placement of peritoneal catheter placement entails:
- knowledge of informed consent,
- proper technique,
- minimizing patient discomfort, as well as
- functional catheter placement.
In addition they should be able to perform independently the following:
To be able to write a prescription, conduct and supervise acute and chronic intermittent hemodialysis
- Entails knowledge of proper indications for hemodialysis,
- knowledge of first dialysis precautions,
- writing of dialysis order which includes choosing dialysis filters,
- estimating dry weight and modification during special circumstances (critically ill child, in-born errors of metabolism),
- choosing dialysate composition,
- understanding and treatment of complications, and
- modifying dialysis prescription for inadequate clearance in chronic hemodialysis patients.
To be able to write a prescription, conduct and supervise acute and chronic peritoneal dialysis:
- Entails knowledge of proper indications of peritoneal dialysis,
- writing orders for peritoneal dialysis which includes dialysis prescription (volume of dialysate, frequency of exchanges, and use of different hypertonic solutions),
- understanding and treatment of complications, and
- modifying dialysis prescription in special situations (lactic acidosis, metabolic disorders) and inadequate clearance in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients
To be able to write a prescription, conduct and supervise continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT)
- Entails knowledge of proper indications of CRRT,
- writing orders for continuous renal replacement therapy (flow rate of dialysate, choosing ultrafiltration rate,
- choosing dialysate composition including the use of bicarbonate based solutions),
- understanding and treatment of complications, and
- modifying dialysis prescription for inadequate clearance in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy
To be able to write a prescription, conduct and supervise slow low efficiency daily dialysis (SLED)
- Entails knowledge of proper indications of SLED,
- writing orders (flow rate of dialysate,
- choosing ultrafiltration rate,
- choosing dialysate composition,
- understanding and treatment of complications, and
- modifying dialysis prescription for inadequate clearance in patients undergoing SLED
To be able to write a prescription, conduct and supervise plasmapheresis
- Entails knowledge of proper indications of plasmapheresis,
- writing orders (volume of plasma replacement,
- choosing rate of plasmapheresis, monitoring,
- understanding and treatment of complications, and modifying plasmapheresis prescription based on the goal of plasmapheresis.
To be able to perform urine analysis at bedside
- To perform correctly urinalysis and interpret findings and to know the limitations of interpretation as applied to patient care
|
Procedure |
O |
A |
P |
SJ |
|
Renal biopsy |
||||
|
Hemodialysis catheter access |
||||
|
Acute peritoneal catheter insertion |
||||
|
Urine analysis |
O- Observed; A- Assisted; P- Performed independently; SJ- Supervised junior colleague
4. TEACHING AND LEARNING METHODS
Clinical postings: Recommended schedule for three years training
The training of the post graduate student shall be a residency program with graded responsibility in the management of patients entrusted to his/her care. The participation of the students in all facets of the educational process is essential. The post graduate student shall take active part in seminars, group discussions, clinics, journal reviews, CPC and clinical meetings. The post graduate student shall also participate in training of post graduates, nursing and paramedical staff. They shall also be involved in research activities pertaining to the subject.
The post graduate student is required to work full time in the Department of Pediatric Nephrology, participate in the patient care and academic and research activities as described below. The trainee should attend not less than 80% (Eighty percent) of the training during the calendar year.
Orientation programme: The post graduate student would first familiarize himself/herself with the faculty of the department and other allied specialties; general working of the hospital, the Wards, admission norms, geography of the hospital, location of the various services, discharge protocol, ordering investigations and other administrative aspects that may be help in them during their training period.
The clinical postings will divided between the out-patient services, sub-specialty clinics, wards, dialysis, intensive care unit and electives.
The training will consist of intensive training in Clinical Nephrology in order to develop the fundamental skills and knowledge required to evaluate, diagnose and formulate management plans for various renal diseases in out-patient and in patient setting and in emergency cases. During the postings in ward, the DM student will be directly involved in patient care and present clinical cases to the faculty and receive one-on-one instruction and feedback in history taking, physical examination and management. The senior DM students will also engage in supervising and teaching junior colleagues. The faculty will interview, examine and discuss assessment and plans with the DM students for all inpatient consultations and emergency cases. The DM student will also undertake 24 hour calls as per the schedule of the department and will report to faculty on call. The student will also learn to counsel the patients and care takers. It will be the responsibility of the DM student to maintain documentation regarding the care of the patients treated in the unit. This will include preparation of discharge summaries, scheduling of treatment protocols for chronic diseases and transplant patients, and preparing medical reports.
During the postings, the DM student will perform various procedures initially under supervision of faculty or senior trainees and later independently like percutaneous renal biopsy of both native and transplanted kidneys, placement of temporary vascular access for hemodialysis or continuous renal replacement therapy, placement of peritoneal catheter for acute peritoneal dialysis, prescribing , supervising and trouble- shooting acute and chronic hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, continuous renal replacement therapy, plasmapheresis and performing urinalysis.
The total period of the course is 36 months. Of this, 30 months will be spent in the pediatric nephrology unit; 6 months will be meant for rotations in related specialties.
Suggested posting schedule Mandatory
- Pediatric Nephrology including hemodialysis service 30 months
- Pediatric Urology/Surgery 1 month
- Adult Nephrology 1-2 months
- Renal Pathology 15 -30 days
Electives (at least three of the below – 3 months)
- PICU/NICU
- Radiology
- Nuclear medicine
- Posting to an external Pediatric Nephrology unit
- Genetics
- Transplantation immunology and diagnostics
(i) Academic sessions: In addition to bedside teaching during clinical rounds and in out- patient setting, formal teaching is necessary. The departments may select a mix of the following: sessions:
Journal club/Review Once a month
Medical audit Once a month
Seminar; lecture Twice in a month
Case discussions Once a week
Interdepartmental case or seminar Once a month
Attend accredited scientific meetings (CME, symposia, and conferences)
Additional sessions on basic sciences, biostatistics, and research methodology, teaching methodology, medical ethics and legal issues related to pediatric nephrology are suggested.
a) Journal Club/Review: Once per month of 1 hour duration-. The presentation of journal club includes a brief review of the scientific context of the paper, the data, an analysis thereof, and a critique/discussion of the experimental approach/study design and results. In journal review, relevant articles from recommended journals are reviewed. Each post graduate student shall present at least 6 journal club/reviews in one academic year and attend at least 12 others.
b) Seminars/Topic review: Seminar twice every month of 1 hour duration. Aim is to provide didactic seminars on topics that cover the broad field of Pediatric Nephrology and includes basic sciences relevant to the topics being discussed. Each post graduate student shall present at least 6 seminars/symposia in one academic year and attend at least 12 others.
c) Case presentation in the ward once a week for one hour. Post graduate students will present a clinical case for discussion before a faculty and discussion made pertaining
to its management and decision to be recorded in case files. Alternatively, a case is selected and presented by a post graduate student (with faculty input) from those encountered by the post graduate student in hospital and in outpatient clinics. Important literature review associated with the case may also be presented. The case is analyzed in order to make key teaching points. Each post graduate student shall present at least 6 clinical cases in one academic year and attend at least 12 others.
d) Clinical renal pathology Conference: Once a month of 1 hour duration. The biopsies performed during the preceding month will be discussed. The post graduate student will summarize the clinical aspects of the case followed by interpretation of the renal biopsy in conjunction with faculty from pathology. Each post graduate student shall present at least 6 cases in one academic year and attend at least 10 sessions.
e) Inter-departmental seminar or Grand Round: Presentation of cases in clinical combined / grand rounds (Neonatology, Pediatrics, Pediatric Surgery, Radiology, nutrition) once in a month. Each post graduate student shall present at least 3 cases in one academic year and attend at least 8 sessions.
f) Mortality and Morbidity/Audit meet: Once a month for one hour to discuss the mortality and departmental statistics.
(ii) Teaching in the out-patient setting, during clinical rounds: The faculty should engage in briefly discussing with the post graduate students various common and uncommon cases presenting in the OPD. There would be at least one consultant-led ward round daily that includes referral in other departments and ICU. This would be a service round with individual case presentation and brief discussion. In addition, at least 02 teaching rounds per week are recommended involving detailed discussion on admitted clinical cases. Besides theoretical aspects, emphasis must be laid on bedside assessment and practical management issues.
(iii) Others: These include non-formal teaching during the discussion on management strategies for specific sub groups of children with renal diseases.
a) Dialysis meets: Once a fortnight for one hour to discuss the various aspects of the children undergoing maintenance hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
b) Transplant meets – once a fortnight for one hour to discuss transplant workup and also discuss management issues in children who have been transplanted.
(iv) Conference, CME’s and Workshops: Participating and contributing to the organization of such meets is desirable. During the 3-year period of training; he/she should attend at least one national or international and one state level meet.
(v) Paper Presentation/ Publication: During the training programme, the trainees must have presented at least one paper in a national or international conference and have at least one publication in a peer reviewed journal.
(vi) Teaching by trainees: The post graduate student will assist and be involved in the teaching of under graduate medical/ nursing students and those training for MD (Paed). He/she will learn the use of various teaching – teaching media (eg. audiovisual aids) in this exercise.
5. LOG BOOK
The DM student shall maintain a log book of the work carried out by them and the training programme undergone during the period of training including details of procedures assisted or done independently by the trainees. The log book shall be checked and assessed periodically by the faculty members imparting the training. Maintenance of performance record in Log book is mandatory. Certified and assessed copy should be made available at the time of practical examination for review by examiners.
Log book should be made to contain:
1. Certificate duly signed by Head of department and Head of Institute stating Dr………….. has worked in department from………to………for a period of 3 years. This performance record book contains authentic record of work done and assessment for last 3 years.
2. Record of training: Name of the trainee; Name of the Hospital; Training period; Name of guide.
3. Posting.
4. Working schedule.
5. Teaching programme.
6. Presentationat academic sessions (Journal club/Review, Seminars, Case presentation/conference, Audit, Teaching activity): Date, Topic/Article name, Prersenter/Attendee, Assessment.
7. Procedures: Date, Name of patient, Type, Complications observed. Mentioned if supervised / performed independently or supervised colleague during the procedure.
8. Participation in Research Activity: name of project, Duration.
9. Conference / Workshop attended: Date/Conference name/Place
10. Paper presentation / Publications.
ASSESSMENT
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT, during the training programme
Formative assessment (periodic, multiple) is an internal assessment by the teaching faculty of the department. The faculty should assess medical knowledge, patient care, procedural & academic skills, interpersonal skills, professionalism, self-directed learning and ability to practice in the system.
Each trainee should attend regular appraisal meetings and reviews of their academic performances, competence progression and workplace based assessments by the faculty of the department. It is frequent, covers small content areas and provides immediate feedback to the teacher and the taught.
Assessment
• Personal attributes 3-6 months
• Clinical skills and performance 3-6 months
• Academic activities 3-6 monhs
• Theory assessment End of 12 and 24 months
• Practical assessment -do-
Personal attributes includes a broad assessment of general attitude, interest in work, initiative, responsibility and reliability, organizational ability, communication skills, professional attitude and team work.
Assessment of academic activities includes Journal based / recent advances learning, participation in departmental and interdepartmental learning activity, external and outreach activities and attending /presenting abstracts in CMEs and conferences.
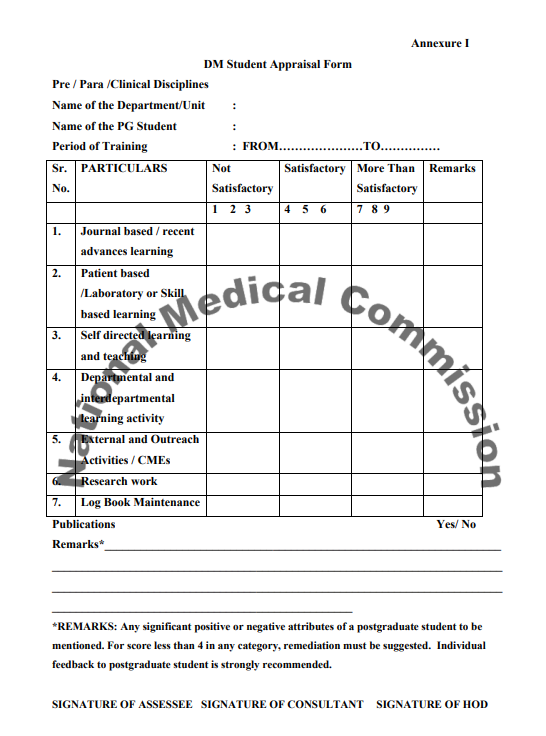
Clinical skills and performance, academic performance and personal attributes shall be graded on a scale of 1 to 9 listed in DM student appraisal form (Annexure I). The academic presentations shall be graded at the time of presentation of the faculty in-charge. Evaluation on clinical skills including competency in procedures and personal attributes shall be done by the Unit in-charge at the end of every quarter.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT, namely, assessment at the end of training
The summative examination should be carried out as per the Rules given in POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL EDUCATION REGULATIONS, 2000. The Post graduate
examination shall be in two parts and will be as per the details given in Post Graduate Regulations, 2000.
Summative evaluation (terminal, single) is a combined assessment by the internal and external examiners designated by the NMC/Medical University of the State at the end of the course.
The DM examination shall be in two parts: Theory and Clinical / Practical and Oral/viva voce Examination.
1. Theory: There shall be four theory papers of three hours duration as follows:
Paper I: Basic Sciences as applied to the subject including physiology, anatomy, embryology epidemiology, pharmacology, biochemistry, pathology, genetics and biostatistics
Paper II: Clinical nephrology
Paper III: Dialysis, Transplantation and Nephro-urology
Paper IV: Recent advances in Pediatric nephrology
The theory examination shall be held in advance before the clinical and practical examination, so that the answer books can be assessed and evaluated before the commencement of the clinical/practical/oral examination.
Evaluation: The answer books shall be valued by two examiners or as per Rules of the University concerned. The average of the two marks secured by the post graduate student will be taken into account. If the difference between two marks exceeds 10%, the answer scripts shall be valued by the third examiner. The average of the nearest two marks shall be considered as the final mark.
2. Practical: The practical examination should consist of the following and should be spread over two days, if the number of candidates appearing is more than five. There will be one internal and two external examiners.
1. One long case: History taking, physical examination, interpretation of clinical findings, differential diagnosis, investigations, prognosis and management.
2. 2 short cases
3. Ward rounds for clinical, procedural and communication skills (4 cases)
4. Log Book Records and day-to-day observation during the training
Viva-voce Examination:
– Viva – Research related
– Instruments/Drugs
– Radiology/Nuclear imaging/Investigations
– Renal Pathology
RECOMMENDED READING:
Books (latest edition)
1. Diagnostic Atlas of Renal Pathology, Fogo, Agnes B 7th ED. Elsevier
2. Clinical Dialysis, Nissenson, Allen R,4th ED. McGraw Hill.
3. Hypertension companion to to Brenner & Rectors the Kidney, Oparil, Suzanne, Elsevier.
5. Disease of the Kidney & Urinary tract ,Schrier,Robert W, Vol I, Lippincott.
6. Disease of the Kidney & Urinary tract ,Schrier,Robert W, Vol II, Lippincott.
7. Disease of the Kidney & Urinary tract ,Schrier,Robert W, Vol III, Lippincott.
8. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, Feehally, John, Mosby.
10. Seldin and Giebischs the Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology, Alpern, Robert. J, Vol I, Academic Publisher.
11. Seldin and Giebischs the Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology, Alpern, Robert. J, Vol II, Academic Publisher.
12. Comprehensive Pediatrics Nephrology, Geary, Denis. F (ED), 1st ED. Elsevier.
13. Evidence‐Based Nephrology, Molony, Donald. A, John Wiley.
14. Handbook of Dialysis, Daugirdas, John. T, Lippincott.
15. Oxford Handbook of Dialysis,Levy, Jeremy,2nd ED. Oxford, 2007
16. Ganongs Review of Medical Physiology, Barrett, Kim. E (et al), McGraw Hill.
17. The Kidney, Brenner & Rector ‐ Saunders.
18. Critical Care Nephrology, C. Ronco, Saunders.
Journals
3-5 International and 02 national journals (all indexed)